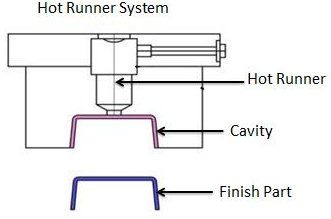
When people hear “medical device,” they often think of strict, hospital-grade materials. However, the broader health and wellness industry uses a wide range of products. Many of these items successfully and safely use food grade plastics. Understanding where these materials are appropriate is key to smart, cost-effective product design.
At our medical molding facility, we work with both medical-grade and high-quality food-grade resins. The choice always depends on the product’s intended use, risk level, and regulatory path.
This blog explores the common and practical applications of food-grade plastics within health, wellness, and the peripherals of the medical field. We will focus on concrete product examples to show where these materials make perfect sense.
Food Grade vs. Medical Grade
First, a crucial reminder from our food-grade vs. medical-grade plastic material discussion: Medical-grade plastic is a superset of food-grade plastic. It passes all food safety tests plus intensive biological safety tests, like ISO 10993.
Use Medical Grade Plastic when the device is classified as a medical device (diagnosing, treating, curing a disease) and/or has direct contact with internal body tissue, the bloodstream, or requires sterilization.
Food-grade plastic can be suitable for products that contact intact skin, hold consumables, or are general wellness items not making medical claims.
Common Applications of Food-Grade Plastics in Health & Medical Spaces
1. Consumer Health & Wellness Products
These products support a healthy lifestyle but are not regulated as medical devices.
- Smart Water Bottles & Hydration Trackers: The interior that holds liquid must be food safe. The outer casing and electronics housing often use food grade or general-purpose plastics.
- Vitamin & Pill Organizers: The compartments that store daily supplements are made from food grade polypropylene (PP) or similar materials.
- Portable Blender Cups & Shaker Bottles: The cup that holds smoothies or protein drinks is typically food grade plastic.
- Humidifier & Air Purifier Tanks/Reservoirs: The water tanks in these appliances are commonly made from food safe materials to prevent leaching into the mist or water.
- Fitness Equipment Accessories: Hand grips, water bottle holders on treadmills, and components of home gym equipment often use durable, food-contact-safe plastics.
2. Non-Critical Medical Device Accessories & Enclosures
These are parts of a system that do not directly interact with the patient in a critical way.
- Device Housings & External Covers: The outer shell of a patient monitor, ultrasound unit, or dental equipment often uses robust, chemical-resistant food grade ABS or PC. It protects the internal electronics but only contacts the user’s hands or the environment.
- Handles and Grips: Non-powered surgical instrument cases, or handles on large medical carts and beds can utilize food grade materials.
- Storage Bins & Carts: Bins used in hospitals to store clean supplies (like bandages or linens) in patient rooms or clinics are often molded from food safe, easy-to-clean high-density polyethylene (HDPE).

3. Packaging for Health-Related Goods
Primary packaging often requires food-grade or higher compliance.
- Supplement & Nutraceutical Bottles: Containers for vitamins, probiotics, and herbal supplements require food-grade materials to ensure the contents are not contaminated.
- Medical Grade Nutrition Packaging: Liquid nutritional shakes for patients, often administered via a feeding tube, use packaging that meets stringent food-grade standards.
- Disposable Cups & Containers: Cups used to dispense medication or sample containers in a clinic setting may use food-grade plastics.
4. Products for Hygiene & Daily Care
These items contact skin or mucous membranes briefly but are considered low risk.
- Electric Toothbrush Handles: The handle that you hold is commonly made from food-grade or body-safe plastics. The brush head itself may have different requirements.
- Manual Toothbrush Handles.
- Bottle Warmers & Sanitizer Baskets: Parts that hold baby bottles or pump parts use food-grade materials because they contact items that go into an infant’s mouth.
- External Thermometer Casings: The casing of a forehead or ear thermometer uses body-safe plastics, while the probe may have a specialized medical-grade coating.
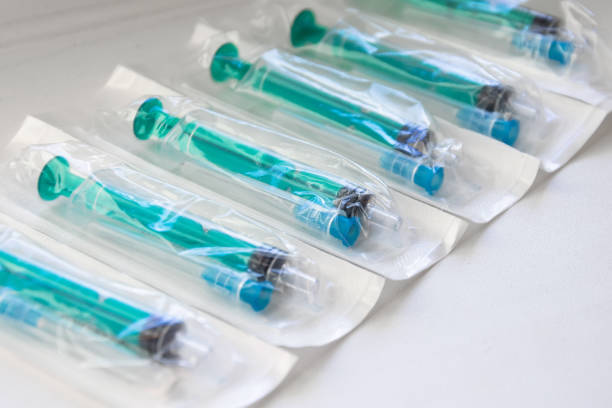
Important Lines That Must Not Be Crossed
It is vital to know where food grade plastic is NOT sufficient. Using it here would be unsafe and illegal.
- Any Implantable Device: Pacemakers, joint replacements, surgical meshes.
- Devices Contacting Blood or Internal Tissue: Syringes, IV catheters, surgical instruments that cut tissue, blood collection tubes.
- Devices Requiring Sterilization: Any product that must be sterilized (by autoclave, gamma radiation, EtO gas) for single-use or reuse needs plastic rated for that process, which is a medical-grade property.
- Drug Delivery Components: The barrel of a syringe, the reservoir of an inhaler, or an IV bag port that contacts the drug product directly require USP Class VI or similar medical-grade biocompatibility testing.
Conclusion: Choosing with Clarity and Purpose
Food grade plastics play a significant and valuable role in the health and wellness ecosystem. They are the ideal, cost-effective choice for a wide array of products that support health, house electronics, store consumables, or contact intact skin.
The key is intentionality and clarity. By clearly defining your product’s function, contact points, and regulatory status, you can make the correct material choice. This ensures safety, manages cost, and streamlines your path to market.
Need help selecting the right plastic for your health or wellness product?
Our engineering team has expertise in both medical-grade and high-performance food-grade molding. We can help you navigate the specifications to find the perfect, compliant, and practical material solution for your specific application.
Contact us today to discuss your product requirements.