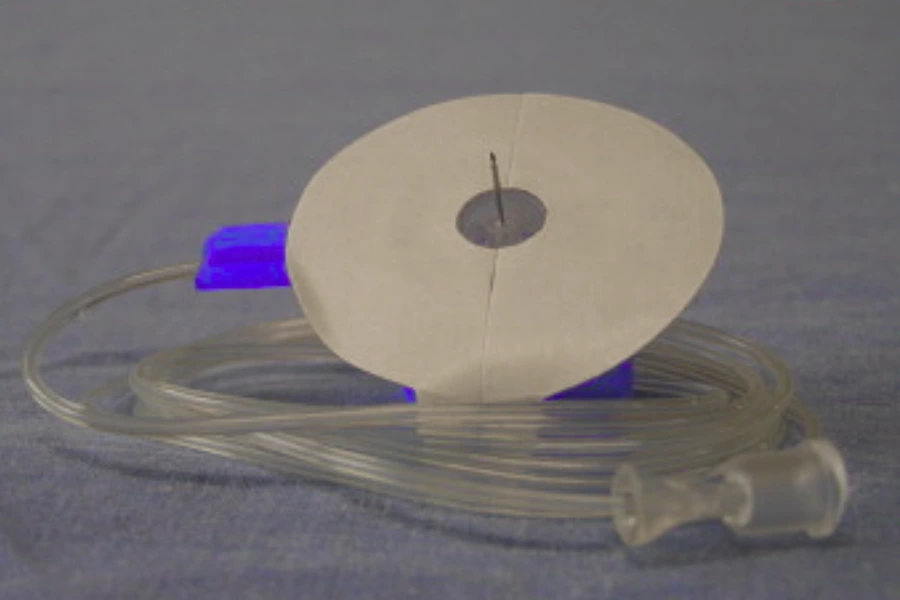
A medical IV set is a controlled fluid delivery device used to administer fluids or medications directly into the bloodstream through an intravenous access.
It provides a defined physical pathway that supports flow regulation, sterility control, and connection stability during intravenous therapy.
An IV set does not generate delivery pressure or dosing logic.
Its role is to maintain predictable fluid behavior under gravity or pump-assisted conditions.
What an IV Set Does in Intravenous Therapy
A medical IV set is a disposable device designed to transport fluids from a container to a patient’s vein through an IV catheter.
Its function is limited but essential:
- forming a continuous and sealed fluid path
- allowing controlled adjustment of flow resistance
- supporting safe interaction with external control systems
IV sets operate as passive components.
They respond to pressure differences rather than creating them.
Key Components That Make an IV Set Function
1.How the IV Set Connects to the Fluid Container
The spike pierces the IV bag or bottle to establish fluid entry into the system.
Its design balances penetration force, sealing reliability, and material rigidity.
A stable container interface is required to prevent leakage and air ingress during infusion.
2.How the Drip Chamber Controls Air and Flow Visibility
The drip chamber serves two functions.
It provides visual confirmation of flow and acts as a buffer zone that separates air from the fluid path.
Its fixed position above the tubing allows air to remain trapped while liquid continues downstream.
3.How Tubing Maintains a Stable Flow Path
IV tubing forms the primary conduit between the drip chamber and the patient.
Its inner diameter, wall thickness, and flexibility directly influence flow resistance and delivery consistency.
In manufacturing practice, maintaining these dimensions within tight tolerances is critical.
Variations introduced during molding or extrusion can lead to unstable flow behavior in clinical use.

4.How Flow Is Adjusted During Infusion
Flow regulation is achieved by increasing or decreasing resistance within the tubing.
A roller clamp applies controlled compression that narrows the internal flow path.
Because resistance changes are nonlinear, small mechanical adjustments can significantly alter flow rate.
5.How the IV Set Connects to the Patient
The distal connector links the IV set to the catheter using standardized interfaces such as luer locks.
This connection must remain secure under continuous flow and patient movement.
Dimensional accuracy at this interface directly affects sealing performance.
In IV sets, even minor geometric deviations can increase leakage risk or connection instability.
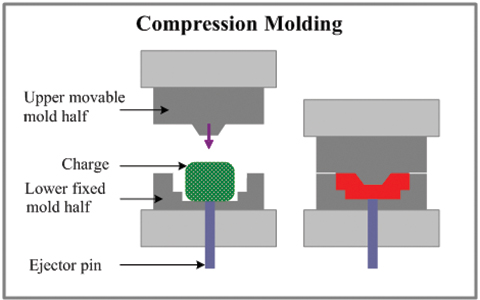
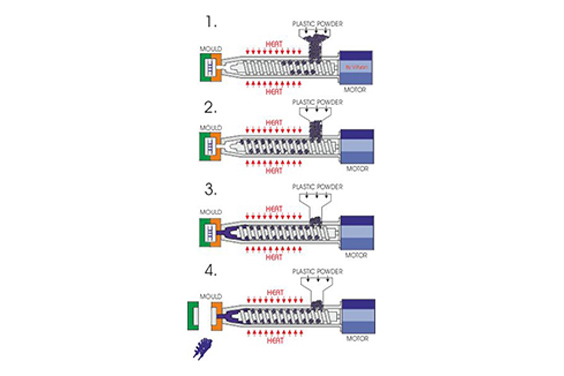
This is why medical-grade injection molding processes are commonly used to control repeatability in high-volume IV components.
How an IV Set Delivers Fluid Step by Step
1.Preparing the IV Set for Fluid Delivery
The IV set is connected to the fluid container under sterile conditions.
Tubing is primed to remove air before patient connection.
Priming establishes uninterrupted fluid continuity.
2.How Fluid Starts Moving Through the System
In gravity-based systems, fluid movement begins when a height difference exists between the container and the patient.
This height difference creates hydrostatic pressure.
Raising or lowering the container alters flow rate by changing pressure magnitude.
3.How Flow Rate Is Controlled During Use
The roller clamp adjusts resistance to balance pressure and flow.
Precise adjustment requires attention because small changes can produce noticeable flow variation.
When infusion pumps are used, the IV set provides a compliant pathway while the pump supplies controlled pressure and timing.
4.How Fluid Enters the Vein Safely
Fluid enters the vein through the catheter as a continuous stream.
Any interruption, air inclusion, or pressure instability can affect delivery safety.
System integrity depends on stable connections and uninterrupted tubing geometry.
Common IV Set Designs and When They Are Used
Vented IV Sets for Rigid Containers
Vented IV sets allow air to enter rigid containers as fluid exits.
This prevents vacuum formation that would otherwise stop flow.
They are required when container walls cannot collapse.
Non-Vented IV Sets for Flexible IV Bags
Non-vented IV sets rely on container collapse to maintain pressure balance.
Flexible bags deform as fluid volume decreases.
Complete priming is required to avoid air introduction.
Filtered IV Sets for Particle and Air Control
Filtered IV sets incorporate inline filters to remove particulate matter or air bubbles.
Filter selection depends on application requirements and flow characteristics.
Gravity IV Sets for Routine Infusions
Gravity IV sets operate without active pressure generation.
They are suitable when moderate flow stability is acceptable.
Operator adjustment is required to maintain consistency.
Strengths and Limitations of Medical IV Sets
Where IV Sets Perform Well
- simple and predictable fluid behavior
- compatibility with gravity and pump systems
- visual confirmation of flow
Practical Limitations to Consider
- flow precision depends on resistance adjustment
- performance varies with height and tubing geometry
- aseptic handling remains critical
Where Medical IV Sets Are Typically Used
Medical IV sets are used for:
- hydration therapy
- medication infusion
- nutritional delivery
- blood and plasma administration
They form the baseline delivery structure in intravenous systems.
Why Manufacturing Quality Matters for IV Sets
The functional stability of an IV set depends on consistent material behavior and dimensional control.
Flow resistance, sealing reliability, and connector performance are all influenced by how precisely components are formed.
In real manufacturing environments, IV set components are typically produced using medical injection molding to achieve repeatable geometries at scale.
Cleanroom-controlled molding and assembly processes help reduce contamination risk while maintaining dimensional consistency.
SeaSkyMedical works with medical device manufacturers to support the production of IV-related components through medical injection molding and cleanroom manufacturing.
This manufacturing approach aligns with the functional requirements of IV sets where predictable fluid behavior and connection stability are required.
Key Takeaways
Medical IV sets function as passive control elements within intravenous delivery systems.
They regulate flow behavior through geometry, resistance, and sealing rather than active pressure generation.
Understanding these mechanics clarifies how IV sets interact with gravity- and pump-based infusion methods.