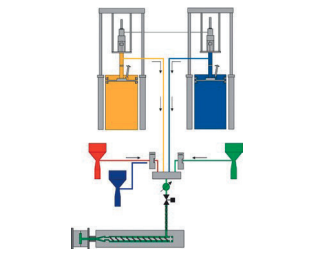
Choosing a medical device manufacturer is a technical decision shaped by regulation, process stability, and long-term production realities. The questions below are commonly used to evaluate whether a manufacturer can support medical device production under controlled and repeatable conditions within a medical device contract manufacturing framework.
This is decision-support content. It focuses on how manufacturers operate in practice rather than how they describe themselves.
What These Questions Help You Confirm
These questions help determine whether a manufacturer’s systems can support compliant production from prototype through volume manufacturing. They are typically used during supplier qualification, early engineering discussions, and contract review stages.
The goal is to confirm process readiness rather than marketing alignment.
Evaluating Manufacturing Experience for Your Device
What experience do you have with similar medical devices?
Experience is most relevant when it aligns with product geometry, material behavior, and regulatory exposure. General molding capability alone does not guarantee suitability for medical components.
When reviewing experience, it’s common to confirm:
- Parts with comparable wall thickness and tolerance ranges
- Use of medical-grade thermoplastics under validated conditions
- Exposure to disposable or single-use medical components
Manufacturers specializing in medical plastic injection molding are typically more familiar with validation constraints, material traceability, and tooling wear patterns specific to medical programs.
How Quality Is Controlled During Medical Production
How is quality controlled throughout production?
Quality systems are expected to extend beyond final inspection. In medical manufacturing, process control is typically built into each production step.
Areas that usually indicate maturity include:
- Defined in-process inspection points
- Lot traceability linking raw material to finished parts
- Clear handling of nonconforming output
In OEM medical component manufacturing environments, these controls are integrated into daily production rather than treated as separate quality events.
How Do You Stay Ready for Audits and Inspections
Audit readiness reflects process consistency rather than documentation volume. Facilities producing medical components commonly maintain audit records as part of routine operations.
This often includes:
- Controlled work instructions tied to specific processes
- Operator training records linked to equipment and tasks
- Internal corrective action workflows
Such practices are standard in cleanroom medical manufacturing environments where process drift directly affects compliance risk.
Engineering Support Before Tooling and Production
How Is Design Adjusted for Stable Manufacturing
Design for manufacturability is used to reduce tooling revisions and stabilize production output. In medical programs, design decisions often affect validation timelines.
Common focus areas include:
- Uniform wall thickness to control shrinkage
- Draft angles suitable for multi-cavity tooling
- Tolerance stack-up across assembled components
Manufacturers supporting early product development and injection molding design typically identify these constraints before tooling release, reducing late-stage engineering changes.
Supporting Volume Growth Without Process Changes
Can production scale without changing core processes?
Scalability depends on process stability rather than machine count alone. Increasing output while maintaining validation status requires controlled expansion.
Indicators of scalable manufacturing often include:
- Documented process windows
- Tooling designed for higher cavitation
- Defined capacity planning methods
This approach is commonly applied in medical consumables injection molding, where demand increases after initial market entry.
Managing Medical-Grade Materials and Supply Risk
How are medical-grade materials selected and managed?
Material selection affects performance, regulatory acceptance, and long-term supply continuity. Medical-grade plastics are typically managed under stricter change control.
Evaluation points often include:
- Approved supplier lists
- Material batch traceability
- Defined material change notification procedures
These controls are foundational to medical plastic injection molding operations.
Cleanroom Use and Environmental Controls
What production environments are used?
Not all medical components require cleanroom conditions. When required, cleanroom classification directly affects process layout and cost structure.
Manufacturers operating ISO Class 7 or ISO Class 8 environments typically define:
- Controlled material flow paths
- Personnel gowning and access procedures
- Environmental monitoring routines
These conditions support precision molding, secondary operations, and packaging under controlled contamination levels.
Support After Production Launch
What support is provided after production begins?
Medical device manufacturing often continues to evolve after launch. Ongoing support helps manage design updates, regulatory changes, and volume adjustments.
Post-production support may include:
- Process optimization and yield improvement
- Tool maintenance and refurbishment planning
- Technical documentation updates
This lifecycle approach is typical in medical OEM injection molding solutions intended for long-term programs.
Balancing Cost Control and Manufacturing Risk
How is cost controlled without reducing process stability?
Cost efficiency in medical manufacturing is typically achieved through process refinement rather than material substitution.
Common methods include:
- Cycle time optimization
- Yield improvement through process control
- Preventive maintenance scheduling
These measures reduce total cost of ownership while maintaining compliance.
Using These Questions During Manufacturer Selection
These questions are used to compare manufacturing systems rather than company size or claims. Clear answers supported by process detail often indicate manufacturing maturity.
Manufacturers offering one-stop medical molding services usually integrate these evaluation areas into a coordinated production workflow.
How SeaSkyMedical Aligns With These Evaluation Criteria
SeaSkyMedical operates as a medical injection molding manufacturer supporting programs from prototype development through production. Its services commonly include mold design, medical-grade material selection, precision molding, cleanroom production, and packaged delivery under controlled quality systems.
This operating model aligns with the evaluation criteria outlined above rather than replacing them.
Next Steps for Technical Review
For projects requiring controlled medical plastic manufacturing and transparent process management, further technical discussion is typically the next step.