These days, there is a lot of discussion in engineering circles about micro molding, micro molding, or even micro molding. This reflects the growing need for high precision, micro-featured plastic parts from designers and manufacturers. As a result, there are numerous articles in trade publications addressing this new market for injection molding that use a variety of terminology, which might be confusing.
What is Micro Molding?

Micro molding is a technique for shaping and forming thermoplastics to produce items, sections, and components that frequently weigh less than a gram and have a diameter or dimension of only a few millimeters. The components are defined by more than just their size, though. It also refers to accurately, consistently, precisely, and efficiently manufacturing large quantities of these components, which are frequently quite sophisticated and complex.
The “micro intolerance” is one aspect that influences whether micro injection molding is used. This is a measurement of how closely the measurements must match the design in order to be used, or more simply, how small the margin of error must be. In some circumstances, the molded part must have a tolerance of less than 1/1000th of an inch when using micro molding. It is frequently possible to make small parts with less exact tolerances using conventional injection molding.
What Is the Size of Micro Molded Products?
A specific type of plastic injection molding called micro molding is used to create exceedingly small parts. Finished components can readily weigh less than 1 gram and have a cross-section smaller than 1 mm.
Types of Micro Molding

- Micro Insert Molding
The capacity of any micro-molder to carry out other conventional injection molding procedures at the micro size is a crucial component. The need for a micro-sized lead frame and insert molding is constantly increasing, and these procedures must adhere to the same size and tolerance standards as conventional micro-molding.
It’s crucial to have the capacity to consistently and accurately overmold a micro-sized part on an incredibly small insert. The success of the semiconductor and microelectronics industries depends on this process.
There are other types of inserts that can be micro molded besides metal ones. It refers to the ability to shape other polymers in and around a wide range of other materials, including ceramic, glass, textiles, film, and foil. The mold must be extremely exact in order to feed, cut, position, and shut off on this brittle and sensitive material. To protect the insert and maintain the part’s strict tolerances, the molding process needed consistent control.
- 2-Shot Micro Molding
The capacity to simultaneously form two different materials on the same part expands the capabilities of micro molding. One mold cycle is all that is needed thanks to the coordinated firing of the two distinct thermoplastic resins. This technique frequently results in the addition of useful aesthetic or functional features, labor cost savings, or assistance in strengthening the item.
- Micro Metal Injection Molding
Although miniaturization is a current global trend, there is still a lot of progress being made in the development of suitable production techniques for materials like metal and ceramic. Micro Powder Injection Molding (MicroPIM), which has already attained a spectacular technological level and the first successful applications have hit the market, is a promising solution. Micrometer-sized features have been produced using a variety of metals (steel, iron alloys, copper, tungsten, etc.) and ceramic powders.
One of the most important elements affecting surface quality and accuracy is powder particle size. Two-component and in-mold MicroPIM is being developed as a means of advancing micro-manufacturing. With the added benefit of lower assembly costs, both types enable the manufacturing of multi-material, and thus multi-functional, items.
- Micro Plastic Injection Molding
Micro molding is a molding technique used to create plastic parts with tolerances between 10 and 100 microns for shot weights between 1 and 0.1 g. Manufacturers can make intricate tiny geometries with the highest degree of accuracy and precision thanks to this molding method. The first step in the micro molding process takes place in the tooling department, where a mold with a cavity made to resemble the desired object is made. Rapid injection of thermoplastic or resin into the cavity creates the component or part at a fast rate of speed.
- Micro Transfer Molding
A patterned elastomer is used as a stamp, mask, or mold in the process of micro transfer molding (TM), a type of soft lithography. The technique of micro transfer molding is well-known for its applications in the microfabrication of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) devices as well as its use in the fabrication of three-dimensional structures on a microscale level. Techniques like micro transfer molding and other soft lithography techniques have drawn more interest due to the ongoing drive to miniaturize scientific and technical devices. Microtransfer molding may be used to produce scientific apparatus, consumer goods, and biomedical equipment.
One of the most prominent areas of use for soft lithography methods like micro transfer molding is the growing popularity of microfluidic devices. The construction of numerous new sorts of devices and the ability to make existing devices more compact would both be made possible by the capacity to create three-dimensional microfluidic systems. A rising range of applications, including polymer-based integrated optical circuits, artificial bones, integrated microfluidic systems, photonic crystals, and catalytic reactors, have demonstrated interest in producing microstructures in recent years.
What is Micro Molding Process
It takes more than merely operating a tiny machine to perform micro molding. Controlling heat in the micro mold is the key to producing numerous tiny parts that are very near to one another. Micro injection molding machines have more accurate digital microcontrollers and sophisticated temperature sensors than their larger cousins to accomplish this.
The micro injection molding machine’s barrel is considerably smaller than that of the larger one. As a result, cleaning is quick and simple when switching to new material. The micro molding machine can cycle considerably more quickly with micro injection while using much less resin. This is its biggest benefit. This reduces production time and costs significantly.
Advantages/ Features of Micro Molding

The maximum clamping force for small injection molding machines like our Babyplast 10/12 is 10 tonnes. These machines provide a product developer with five key benefits when producing small parts.
- Mold tools cost about 40% less than full-sized equipment since they are significantly smaller and less expensive.
- It uses substantially fewer raw materials during micro molding. This includes any residual resin in the barrel, gate, and runner systems, as well as any other materials used to produce the part.
- Utilizing an online digital database that can store 1,000 different work set-up settings speeds up changeovers. Additionally, flushing out the old resin from the system to get the machine ready for new material is simpler and quicker.
- In order to accurately regulate the mold’s temperature during production, hot runner systems are employed.
- More rapid cycle times. Micro molding machines have short, compact barrels, as well as short gates and runners. In contrast to their larger counterparts, even multi-cavity molds can cycle significantly more quickly.
Disadvantages of Micro Molding
Micro-sized pieces present a significant difficulty for the molder in a few specific applications.
- It is more difficult to machine into the tool steel with small cavities with minute features and thin walls. To create small mold tools, we, therefore, utilize polished stainless steel H13 or NAK80. Due to the small grain and dense molecular structure of these steels, we are able to create fine features with high accuracy and precise tolerances using multi-axis CNC machines.
- When micro-molding, resins behave differently from their full-sized equivalents. This is due to resins being subjected to severe shear stresses as a result of having to quickly fill extremely small voids. Since resin temperature and injection pressure have a direct impact on sheer, it’s crucial to employ specialized micro-machines that can be finely calibrated in order to get the best results.
What Industries Need Micro Molded Parts

Medical And Healthcare Industries
Without a doubt, the majority of processes in the field of medicine demand a high level of accuracy. As a result, the majority of the time, extremely sophisticated and compact medical devices like medical plastic components must be employed. As a result, micro molding is frequently utilized in the production of medical devices like catheters, diagnostic systems, and optical and hearing aid components, and is particularly useful for the instruments used in minimally invasive procedures. For instance, aortic procedures, neurosurgeries, etc.
It should be noted that new kinds of microfluidic systems are gaining popularity and becoming more and more commonly used in a variety of medical procedures (including Point-Of-Care applications). It is not surprising that, according to “Mordor Intelligence,” the medical industry has almost a fifth of the global market for micro injection molding.
Electronic Industries
Due to the shrinking size of contemporary electronic products, this industry is also becoming more and more dependent on high precision and complexity. The advantages of micro molding can be used in the production of numerous electrical components.
One example might be micro-optics (e.g., manufacturing laser-based devices, smartphones, lenses, prisms, etc.). Additionally, there are microelectronic parts for computers, communication technologies, musical instruments, and other microelectronic disciplines, such as connections, switches, plugs, and computer chips.
Micro molding production is frequently used for microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). The demand for inventive micro molding in manufacturing processes is rising because the sector is itself in a growing phase. For instance, the demand for MEMS is greatly increased by the fact that BioMEMS (Biomedical Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) are currently the subject of extensive research and that possible Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) and Point-of-Care diagnostic prospects have already been implemented.
The fact that the electronic sector accounts for little more than a fifth of the global micro injection molding market suggests that the electronic industries have grown dramatically as a result of the quick development of contemporary technology (ibid).
Automotive Industries
For the production of vehicle parts, which usually demand light and compact components, micro injection molding is widely employed. The automotive sector uses micro molding for a variety of additional items that are vital to the automobile industry, including different clips, washers, door locking mechanism parts, various buttons, switches, and even the production of tiny plastic gears. There is no surprise that the automobile sector, which is enormous and necessitates numerous tiny parts, derives the greatest value (nearly a third) from micro molding (ibid).
What Type of Plastic is Used in Micro molding
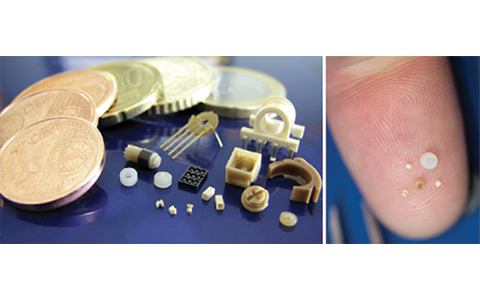
The materials that can be employed in micro molding are extremely diverse. But there are undoubtedly some important considerations to keep in mind when selecting materials, such as mechanical properties (what are the anticipated working conditions, high-heat scenarios, and hygroscopic properties?) cost, cosmetic appeal, and compatibility (interaction with other biological bodies.
- LCP (liquid crystal polymer)
- PMMA (polymethylmethacrylate)
- COCs (cyclic olefin copolymers)
- PEEK (polyether ether ketone)
- PLA (polylactic acid)
- PGA (polyglycolic acid)
- Polyethylene
- Polypropylene
- Polycarbonate
Machine Used for Micro Injection Molding
Traditional injection molding was used in micro injection molding techniques in the 1980s, but until the middle of the 1990s, there were no dedicated machines. Milacron, Arburg, and Sumitomo Demag now make commercial micro molding systems as micro injection units for standard machines. Wittmann Battenfeld, Babyplast, and Desma are producers of specialized micro injection molding equipment at the same time.
Milacron created two different kinds of micro injection units:
- a two-stage, all-electric unit that uses an extruder and an injection plunger.
- a 14 mm screw-equipped, all-electric injection unit for injecting polymer melt into a mold.
To ensure high levels of dosing accuracy, Arburg created a micro injection molding machine with an 8 mm injection. A second screw is added to this kind of machine, and it is in charge of melting and evenly mixing the material. A specialized micro molding injection unit for micro items weighing between 5 and 0.1 g was created by Sumitomo Demag.
The Challenges of Micro Injection Molding

The cost of packaging and small-scale assembly makes up a significant portion of the total cost of any micro-scaled product and is a crucial step in the creation of a microscopic product. Effective assembly and packing are essential for the commercial success of items. The absence of automation in both packaging and assembly for micro-scaled products is the primary cause of these costs.
The majority of micro-assembly tasks need operators to utilize strong microscopes and micro-tweezers to manually pick and insert microscopic pieces. Manual assembly is quite time-consuming and expensive. Operators who assemble such tiny pieces have tightness in their eyes, have exacting standards for the finished product, and must also meet the necessary reliability of its quality.
One of the trickier parts of the injection molding process is tool design. The secret to quality is a double-sided mold manufactured from materials that can withstand high-pressure injection without bending, even after thousands of users. Tooling design is an even bigger challenge in micro molding. There are very few vendors who can meet the requirement for steel tolerances to be within a few microns.
This may also result in “parting lines.” The narrow line of separation on a plastic component where the two sides of the mold meet are known as the parting line. This small seam is usually not a problem with plastics because it is only a few microns wide and is frequently shaved down. The separating line in micro molding can make or break the assembly and have an impact on how well it fits.
The part’s overall strength and precision might be impacted by the gate placement, which is the entrance in the mold through which the plastic is injected into the cavity. To ensure quality and a consistent flow, it is crucial to choose the right location for the opening in the tooling. A vestige, or a small runner of plastic that needs to be clipped when the plastic cools, can be left behind by the gate. Again, accuracy is crucial, so care must be taken when trimming and completing the gate vestige.
What Micro Molding Services Seaskymedical Can Offer?

Micro medical goods play a significant role in medical technology. Seaskymedical, which is a medical plastic injection molding producer, and laboratory consumables manufacturer is skilled at medical micro molding thanks to German and Japanese high-precision injection machines and classes 7 and 8 cleanrooms.
Products with overall dimensions, functional areas, or tolerances in millimeters or even microns can be produced using micro injection molding. 99 percent of our competitors believe that a micro injection is not conceivable, but SeaskyMedical defies them. We are able to produce items with 0.2 mm wall thickness and micro products weighing between 0.1 and 0.5 grams.
- Evaluate the optimal manufacturing strategy
- Product development
- Injection mold material selection guide
- Free Insert mold tooling design and manufacturing
- DFM and flow analysis simulations
- 3D Rapid Prototyping
- CNC plastic machining
- Full-scale contract manufacturing
- Parts assembly and packaging,
- Pad printing & UV welding
Common Questions
- Why is design for manufacturing (DFM) important in micro molding?
Your injection molder should be using DFM concepts to minimize component costs, assembly costs, and production support costs, and to detect the influence of DFM decisions on other elements throughout the entire design and production process, in addition to just estimating manufacturing costs.
The rising complexity of plastic injection molded parts is another factor to consider when choosing a molder that follows DFM principles. To satisfy client demands for quality/price, the design must take tolerance, draught angles, undercuts, and other factors into account.
- The importance of tooling design in micro molding
The success of micro molding is enabled by mold design and mold fabrication. Success in mold-making depends on the experience of the mold designer in a vertically integrated business.
As a medical injection molding company, the mold designers at SeaSkyMedical are well aware of the limitations of micromachining for molds with part characteristics as small as human hair in diameter. To obtain the desired feature and surface finish, they must know the maximum cutter size and depth, the effects of overburning in EDM, and if milling or wire EDM will be more effective.
Together with the abilities required for mold creation, this skill set is practically impossible to outsource.
Conclusion

At SeaSkyMedical, a medical disposable manufacturing company, we manufacture specialized plastics using injection molding and thermoforming for a number of industries, including automotive, medical, and telecommunications. We provide customers across the world with durable, high-quality bespoke plastics at competitive prices per unit and short lead times. We also do contract medical manufacturing.
Genuine micro-molders dependably and effectively generate extreme parts. In the end, a real micro molder is required to match the rigorous standards of contemporary production. If the final product doesn’t satisfy the buyer, the process’ artistry and originality are lost.
Despite the fact that micro molding might seem novel and new, SeaSkyMedical has been producing billions of micro molded parts over the years and has been in the “micro” industry for more than 10 years. It’s where our business began, and it’s where we still expand, experiment, and create. True micro molding is a way of life, a way of thinking, and a way of doing things. If you have any questions, contact us right away!





