Luer connectors are standardized medical fittings used to connect syringes, needles, catheters, and IV tubing.
They are designed to form a continuous fluid pathway using a defined mechanical interface rather than permanent fastening.
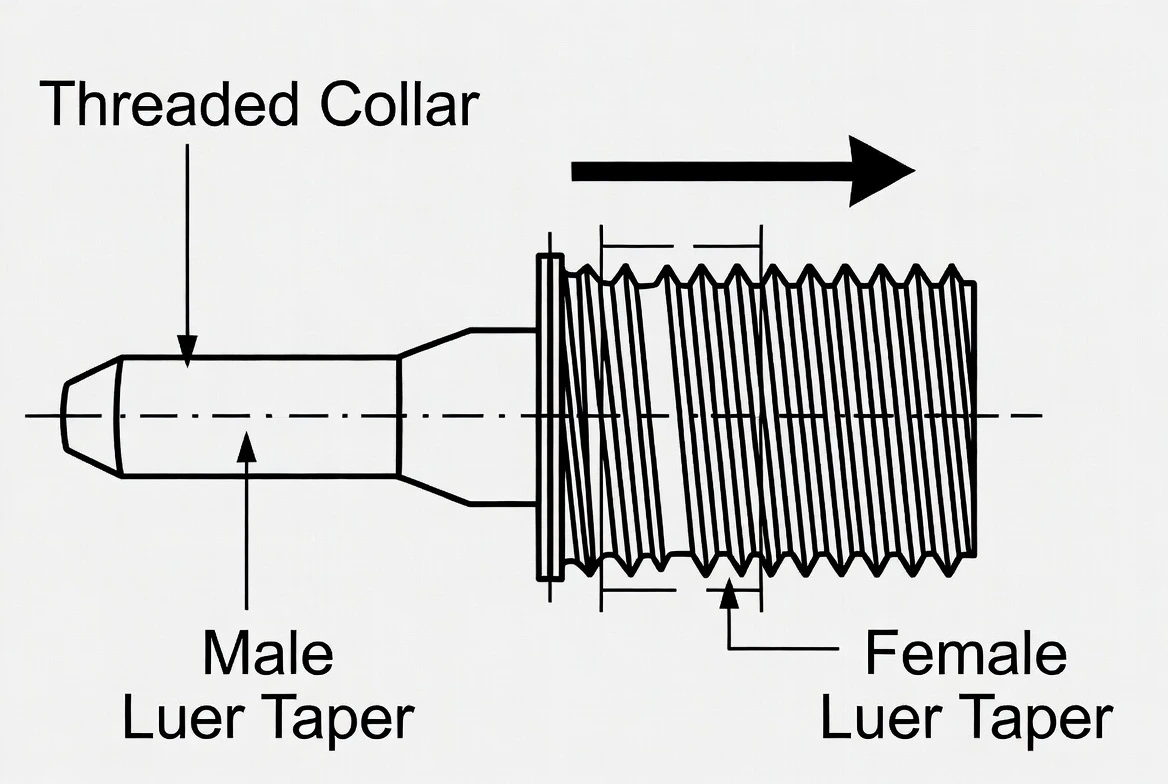
The defining feature of a Luer connector is a 6 percent tapered cone, which allows components to mate through controlled compression and surface friction.
This design enables repeatable connections across a wide range of disposable medical devices.
Luer connectors are typically applied in fluid delivery, aspiration, and sampling systems where consistency and interchangeability are required.
How Luer Connectors Create a Sealed Fluid Path
Why the 6 Percent Taper Is Critical
A Luer connection is formed when a male and female taper with matching geometry are brought into axial contact.
As the components engage, compressive forces develop along the taper surfaces.
These forces generate friction, which both seals the fluid path and resists separation.
In practice, the effectiveness of this mechanism is highly sensitive to taper angle accuracy and surface finish.
Even small deviations in taper geometry can reduce contact area, lower friction, and increase the likelihood of leakage or loosening under load.
How Surface Conditions Affect Connection Stability
Dry Luer connections typically provide higher friction and greater resistance to separation.
The presence of fluid on the taper surfaces reduces friction and can compromise connection stability.
In clinical use, wet connections are common and often unavoidable.
For this reason, reliable performance depends not only on user technique, but also on dimensional consistency and material behavior of the molded components.
Common Luer Connector Designs
Luer Slip Design Characteristics and Limitations
Luer slip connectors rely entirely on taper compression and friction to maintain the connection.
No threads or secondary retention features are present.
They are commonly used in low-risk applications where rapid connection and disconnection are required.
Typical limitations include:
- Reduced resistance to axial pulling forces
- Higher susceptibility to accidental separation
- Limited suitability for high-pressure or critical fluid paths
Because retention depends solely on friction, manufacturing variation has a direct impact on functional reliability.
How Luer Lock Designs Improve Retention
Luer lock connectors incorporate a threaded outer skirt on the male component.
The female component includes lugs that engage with the threads during assembly.
The threaded skirt prevents axial pull-off once engaged.
However, the fluid seal remains dependent on the taper interface, not on the threads.
Common design variations include:
- Fixed skirt designs where the skirt and taper are a single molded part
- Swivel skirt designs where the skirt rotates independently of the taper
Swivel skirt designs reduce torsional stress on connected tubing during assembly.
Why Luer Lock Does Not Eliminate Disconnection Risk
A Luer lock connection does not create a true mechanical lock.
There is no latching mechanism or secondary sealing feature beyond the taper fit.
The threaded skirt does not improve leak resistance.
Its function is limited to preventing direct axial separation.
Luer lock connections remain vulnerable to rotational forces.
In assemblies with perpendicular components or extended attachments, torque can be applied to the connection unintentionally.
Because the threads are coarse, only a small amount of rotation is required to loosen the taper interface.
This effect is amplified in multi-component systems, where leverage can accumulate across connected parts.
How Material Choice Influences Luer Performance
Materials Commonly Used in Medical Luer Components
Most Luer connectors are manufactured from medical-grade thermoplastics.
These materials offer a balance of moldability, chemical resistance, and suitability for single-use applications.
Glass and metal Luer components are used in specialized cases, typically where chemical compatibility or reuse is required.
These materials introduce different tolerances and handling requirements.
Material Deformation and Long-Term Stability
Plastic Luer components are subject to elastic deformation under sustained compressive stress.
Material softness influences how well the taper surfaces maintain contact over time.
Repeated connection cycles can lead to surface wear or minor dimensional changes.
In practice, this can reduce friction and increase the risk of partial separation.
Standards such as ISO 80369-7 place constraints on material properties to limit deformation and improve connection stability under real-use conditions.
Common Failure Modes in Luer Connections
Luer connection failures can occur as complete or partial separations.
Partial separations may appear visually connected while still allowing leakage.
Potential risks include:
- Fluid leakage
- Blood loss
- Air embolism
These risks arise whenever a pressure gradient exists between the fluid pathway and ambient air.
Active pressure or vacuum, such as from syringes or pumps, can significantly increase flow rates during a failure event.
Because Luer connectors are often used in direct vascular access, small connection issues can result in disproportionate clinical consequences.
Practical Considerations for Using Luer Connections
Assembly Practices That Reduce Separation Risk
Luer connections should be assembled by hand only.
The use of tools can damage taper surfaces and compromise sealing performance.
Best practices include:
- Ensuring axial alignment before engagement
- Avoiding cross-threading in Luer lock designs
- Minimizing the total number of connection points
Where possible, connections should be made using clean, dry components.
Monitoring and Protection After Assembly
Once assembled, Luer connections should be protected from unintended forces.
Tubing should be routed to minimize pulling, twisting, or snagging.
Effective monitoring practices include:
- Keeping critical connections visible and accessible
- Inspecting downstream lines for air or moisture
- Using solid caps on unused Luer ports
Early detection of leakage or loosening reduces the risk of escalation.
Why Luer Use Is Restricted by Modern Standards
Luer connectors were historically used across multiple medical systems.
This broad compatibility increased the risk of unintended cross-connections.
The ISO 80369 series of standards was introduced to address this issue.
These standards limit Luer connectors to specific applications, such as intravascular use, and define dimensional constraints to prevent misconnection.
For manufacturers, compliance influences connector geometry, material selection, and tolerance control.
Manufacturing Factors That Affect Luer Reliability
The functional performance of a Luer connector is highly sensitive to dimensional accuracy.
Small variations in taper angle, roundness, or surface finish can significantly alter sealing behavior.
From a manufacturing perspective, key considerations include:
- Consistent taper geometry across multi-cavity molds
- Control of post-molding material relaxation and shrinkage
- Verification of dimensional stability across production batches
In medical applications, Luer components are typically produced in controlled environments to reduce contamination and dimensional variability.
SeaSkyMedical manufactures medical Luer components using precision injection molding processes supported by ISO-class cleanroom production.
This approach allows manufacturers to maintain tighter control over geometry, surface quality, and batch-to-batch consistency.
When Standard Luer Designs Are Not Sufficient
Standard Luer connectors may not meet all system-level requirements.
Custom designs are commonly required when:
- Luer interfaces are integrated into complex assemblies
- Non-standard materials are needed for chemical compatibility
- OEM devices impose tight spatial or tolerance constraints
Early collaboration between design and manufacturing teams helps identify feasibility limits and reduce redesign risk.
Key Takeaways for Medical Luer Applications
Luer connectors appear simple, but their performance depends on tightly controlled mechanical and material factors.
Connection reliability is influenced by design geometry, material behavior, manufacturing precision, and proper use.
Understanding both the capabilities and limitations of Luer slip and Luer lock designs is essential.
Effective risk management requires alignment across design, production, and clinical practice.
Technical Support for Custom Medical Luer Components
For technical discussions related to custom medical injection molding or Luer component manufacturing,
contact SeaSkyMedical for more information.