Parts made of plastic can be produced in a variety of methods. Injection molding and vacuum forming are two of the most widely used plastic forming techniques. Depending on the specific application, both techniques provide distinct advantages. While injection molding is better suited for small, intricate parts and big production runs, vacuum forming, also known as thermoforming, is frequently employed for large-scale designs and shorter manufacturing runs.
Thus while medical equipment parts manufacturers make equipment, medical lab supplies, and surgical disposable product use injection molding, agricultural tools and auto parts require vacuum forming.
Before comparing the methods of Vacuum forming and injection molding let us first understand what each of these means.
What is Vacuum Forming?

The primary idea of this type of plastic processing technology is to heat the flattened plastic hard piece to soften it, then use vacuum adsorption on the surface of the grinding tool to cool it to shape.
Vacuum forming is a common technique in several industries, including plastic packaging, lighting, advertising, and decoration.
Utilizing vacuum forming technology to create plastic products and packaging them with the appropriate tools is known as vacuum bag molding.
Advantages Of Vacuum Forming
- The primary benefits of vacuum forming packaging include reducing raw and auxiliary materials, being lightweight, and transportable, having superior sealing performance, and meeting environmental protection and green packaging standards.
- It does not require an additional buffer and can package any special-shaped item. The packed goods are clear, lovely, and simple to market.
- It is appropriate for automated and mechanized packing, is practical for current management, reduces labor costs, and boosts productivity.
- The vacuum forming packaging equipment basically consists of the following: punch, sealing, folding, and high-frequency machines. Insert cards, suction cards, double foam cards, half foam cards, half-fold foam shells, three-fold foam shells, etc. are different types of packaging materials.
Disadvantages of Vacuum Forming

- The maximum plastic component depth that vacuum forming allows is one of its drawbacks. Shallow plastic bits are required for vacuum forming since deeper ones may twist or warp throughout the procedure. Deeper parts aren’t typically made with vacuum forming, but when it is, additional care must be taken to stretch the plastic first to avoid warping, which raises the cost of production.
- As the material develops bubbles during vacuum forming, distortion is another possibility. Air pockets that enter the material when it is being stretched and molded cause bubbles to form, which can harm the finished products.
- If vacuum forming is the selected manufacturing method, it is crucial that the environment is closely managed so that no extra moisture messes up the process. These bubbles are caused by extra moisture being absorbed into the plastic.
- Vacuum forming can’t produce as many pieces as other methods can.
- The vacuum forming method is inexpensive, but as a trade-off, it is also relatively sluggish and requires precise control.
- Additionally, the speed of vacuum molding must be managed because if the item is allowed to sit for too long, the prolonged exposure to required heat may lead it to spiderweb into fissures.
Process Capabilities of Vacuum Forming
Vacuum forming is one of the most cost-effective thermoforming techniques. A plastic product is a vacuum formed by:
- In an oven, a sheet of thermoplastic material is heated.
- On a mold, the heated sheet is placed.
- The sheet is pulled against the mold to shape it as a vacuum removes air from the mold.
- The produced plastic is removed from the mold and trimmed once it has cooled and hardened.
Applications of Vacuum Forming

Vacuum forming is used in a variety of places like:
- Agricultural elements
Vacuum forming is a common technique in the agriculture sector for producing plastic parts for both heavy-duty machines and transportation vehicles.
- Auto parts
In the automotive industry, vacuum-formed polymers are frequently used for both aesthetic and practical reasons.
Everything you see inside a car, from the dashboard to the door panels, was made using the vacuum thermoforming technique.
- Packaging
The containers used for medical supplies, cleaning supplies, health and beauty goods, and other items are all likely to have been created using a vacuum forming method, just like the food and drink packaging that lines supermarket shelves.
Vacuum Forming Molding Tools

Your tool can be made from a variety of materials. The choice you make will be influenced by a number of factors, like your budget, the size of the order, the desired finish, etc. The most common types of tooling are as follows:
- Wood/MDF – Wood and MDF can be quickly used to build moulds, and they work best for short production runs. Exercise caution because these moulds will deteriorate more quickly than cast ones and the created plastic may show signs of joint wear. Despite being very inexpensive, the material is simple to build with.
- Cast/Molded Tool: This kind of tool can be made of resin casts, fiber-glass, or plaster of paris, which is relatively brittle. This latter material can be polished and sanded to a very smooth texture and is fairly durable. They are also reasonably fast and inexpensive to produce.
- Aluminum: Despite being the priciest material for a tool, an aluminium version is durable and reliable and may be utilised for runs of hundreds of thousands of pieces. It combines great surface hardness, low wear, and efficient heat conduction. The aluminium requires some effort to get a mark-free polish. Aluminum tools can be cast, 3D modelled, and machined, or they can be made by combining the two processes, in which case the tool is cast and then completed on a CNC machine to the necessary level.
Materials Used in Vacuum Forming
The manufacturing process of vacuum forming is suitable for a variety of thermoplastics. The following are some of the most popular plastics:
- Acrylic (PMMA)
- Butadiene with acrylonitrile styrene (ABS)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Glycol made of polyethylene terephthalate (PETG)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Vinyl chloride polymer (PVC)
Waste and Scraps Produced by Vacuum Forming
To get the ideal shape and form of the item being produced it is cut out from the original sheet which causes the accumulation of waste and scraps. If proper preventive measures are not taken it could create pollution.
Cost of Vacuum Forming

Compared to other forming methods, vacuum forming has a number of processing advantages. Low forming pressures are employed, allowing for relatively inexpensive tooling.
Low pressures used during the process allow for the use of inexpensive materials and rather a quick mold creation.
What is Injection Molding?

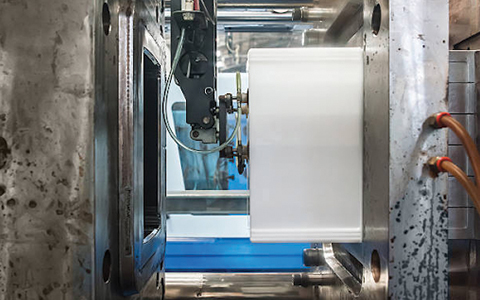
Making plastic parts via injection molding involves melting the plastic material and injecting it into the tool. The most used plastic forming technique is injection molding. An item made of plastic is injected-molded:
- High pressure is used to inject hot, molten plastic between the cavity and core of the mold.
- The chamber of the mold opens and the part is ejected once the plastic has cooled and solidified.
Advantages of Injection Molding
- Fast and high-output production are both provided by the injection molding method. The process is more machine-oriented than other production processes, which results in lower labor costs.
- Multiple materials can be utilized at once, and a variety of colored materials can be employed, which is known to make the design more adaptable.
- Since every component produced is the same, high-quality consistency is a given. Our machines can produce even the smallest pieces while producing as little post-production scrap as possible thanks to the adaptability of clean room injection molding.
Disadvantages of Injection Molding

- One of the few drawbacks of injection molding is that the initial cost of the machinery and tools may be significant.
- Small runs of parts may not be as cost-effective when producing parts in low volumes. Although there are a few design limitations for plastic injection molding, you should be able to work around them by collaborating with our skilled design team.
Process Capabilities of Injection Molding
For production, a mold is made up of two halves: a stationary portion and a mobile portion. The components must be ejected from the mold with ease. Specifically, install the mold in an injection molding machine. The mold’s two components are tightly squeezed together.
Next, the substance is poured into a heated plasticizing screw (also known as an endless screw) in the shape of pellets. The pellets are softened by the screw’s spinning and the temperature, which causes the material to melt into molten plastic.
Prior to injection, the molten and deformable material is held at the front of the screw. Put the mold under high pressure and heat to inject the softened plastic materials.
During this stage, it must be made sure that the material fills the mold to the top before it solidifies. For this reason, we keep sending the material under pressure to make up for the withdrawal that happens as it cools.
Cooling of the entire structure using the mold’s internal cooling channels. The procedure ends with the object being expelled from the mold. Reject the component. Next, repeat the previous step.
Applications of Injection Molding
The majority of mass-produced plastic products are made via injection molding and there are several medical injection molding company because of their high output rate and reliable quality. These goods consist of but are not restricted to :
- Dashboards, bumpers, and grilles are examples of auto parts.
- Electrical connectors, enclosures, and protective sleeving are examples of electronic components.
- Syringes, valves, and dishes are used by medical plastic injection molding producer.
- Plastics used by consumers include toys, bottle caps, and phone cases.
- Seat covers, cushions for chairs, and other furniture components.
- petg injection molding.
Materials Used in Injection Molding

There are ten materials for plastic injection molding that are frequently used:
- Acrylic (PMMA) (PMMA)
- Abutrene butadiene acrylonitrile (ABS)
- Polyamide nylon (PA)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polyoxymethylene (POM)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Thermally flexible rubber (TPE)
- Polyurethane thermoplastic (TPU)
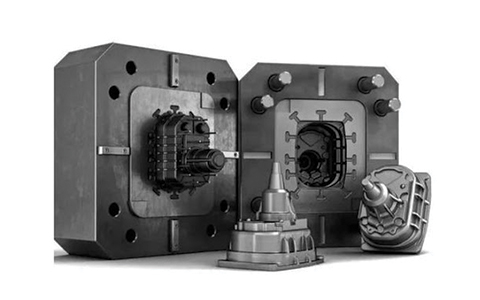
Injection Molding Tools

A two-plate tool is the most popular type of injection mold. There are many varieties of injection molds. The injection mold (A Plate) and the ejector mold are the two primary components of the two-plate tool (B Plate).
A clamping device is used to secure these plates to platens. There is a natural division or split known as the parting line that occurs when these plates come together to form the injection mold.
Waste and Scraps Produced by Injection Molding

There is not much waste created by the injection molding process per unit. The sprue, runners, and molten plastic spilling out of the part’s cavity can all contribute to the debris created throughout the injection mold cycle.
However, you can reduce that waste to zero percent if you use a consistent and verified molding method.
Cost of Injection Molding
Costs for a modest, straightforward, single cavity plastic injection mold typically range from $1,000 to $5,000. Molds that are really huge or intricate may cost up to $80,000 or more.
A common mold that creates a somewhat straightforward component small enough to hold in your palm often costs around $12,000.
Which One Is Better for Your Project – How to Consider?

So, how do we compare vacuum forming and injection molding?
Vacuum Forming:
Production Speed & Quick Turn
Vacuum forming is not nearly as versatile as injection molding. The shaping is done in only one direction since the plastic sheet is stretched over or into a mold, which restricts the shape of the item.
Vacuum forming, on the other hand, may produce items with much thinner walls. Every part is hollow, as evidenced by the vacuum that is developing above. After that, the holes were cut.
Tooling for vacuum forming requires six to eight weeks.
Products Size
Used in small-scale for smaller products. Vacuum forming can produce complex items with a variety of specific features with good tool design.
Precision and Tolerances of Vacuum Forming
Vacuum forming can reach acceptable tolerances, but it is less precise than injection molding as the material is stretched over or into a tool.
Material Considerations
Less material variety, however sheets in ABS, Fire Retardant ABS, HDPE, HIPS, Conductive HDPE, Conductive HIPS, PP, PVC, Clear HIPS, Ultra Violet Stable HIPS, and PETG are easily accessible. Additionally available are sheets with special effects and a variety of colors.
Finishing & Waste
The real product must always be cut out of the plastic sheet; this can be done with a roller, a handsaw, or CNC machining, for example. This can be a somewhat wasteful procedure, depending on the sheet and part sizes. Leftover sheet pieces, however, can be reground and utilized in other procedures.
Injection Moulding:
Production Speed & Quick Turn
Injection molding allows for the inclusion of ribs, bosses, metal inserts, multiple molding materials, side cores, screw thread, holes, and other features in micro-sized objects. Due to the fact that the plastic is injected into the mold, the finished product can almost have any shape. The outcome depends on the choice of materials, how well the injection molding machine is used, and how well the injection mold tool is designed and made.
It takes a considerable time to create injection molding tooling.
Products Size
Mainly used for larger products.
Precision & Tolerances of Injection Molding
Injection molding can produce identical objects repeatedly with exceedingly tight tolerances.
Material Considerations
The variety of materials is enormous! In addition to the wide variety of standard materials, there are also items like thermoplastic rubber, infrared, biodegradable, antistatic plastic, thermoplastic rubber, chemically resistant plastics, and infrared. You can also choose from an infinite number of colors using masterbatch coloring or color compounding.
Finishing and Waste
Each mold tool has “runners” or channels that allow molten plastic to flow to the core and cavity that give the product its shape. If the mold tool has cold runners, each molding cycle will cause them to harden. They can be reground and used again after being removed from each molding. There is no manufacturing waste because, with hot runner mold tools, the plastic in the runners is kept hot and utilized in the subsequent molding.
Conclusion
It’s easy to see that plastic injection moulding offers more benefits as a conclusion to the vacuum forming vs. injection moulding debate. Both have distinctive advantages and disadvantages that may suit the level of output you seek. However, plastic injection moulding is a fantastic option if you need something that is reliable in terms of quality, quantity, and efficiency.