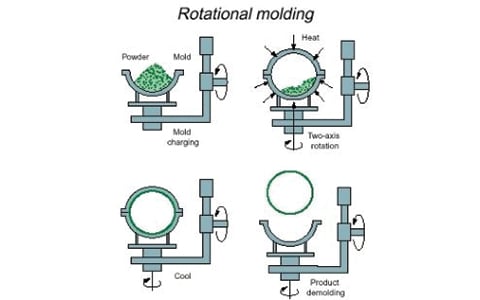
A heated hollow mold that is loaded with a charge or shot weight of the material is used for rotational molding. The material is then slowly rotated, often around two perpendicular axes, causing it to scatter and adhere to the mold’s walls. The mold rotates continuously throughout the heating phase to ensure consistent thickness across the part and to prevent drooping or deformation during the cooling phase.
The method was first employed on plastics in the 1950s, but due to its slowness and restriction to a few specific types of plastics, it was not widely adopted in the early years. The use has grown over time as a result of advancements in plastic powder technology and process control improvements.
As opposed to rotational molding, roto-casting (also known as rota-casting) uses self-curing polymers in an unheated mold yet has slow rotational speeds in common with it. Spin casting should not be confused with shaping self-curing resins or white metal with a high-speed centrifugal casting process.
What Is Rotational Molding?

The plastics molding technique, rotational or roto-molding, is excellent for producing hollow objects. Although it is a casting technique, it does not use pressure as most other plastics processing does. Because the process’s molds don’t need to withstand pressure, they are reasonably cheap and may be produced in relatively short batches at a very low cost.
A wide variety of goods are produced using the roto-molding process. Since almost any shape may be made, the method gives the product designer a great deal of creative freedom. There are literally thousands of uses for moldings, and there are virtually no size restrictions.
Molds, ovens, cooling chambers, and mold spindles are often included in all rotary molding systems. The item is manufactured using molds, which are commonly composed of aluminum in a medical plastic injection molding company. The caliber of the mold being utilized has a direct impact on the product’s quality and finish.
The portion is heated in the oven while being rotated to give it the desired shape. The spindles are mounted to rotate and create a homogeneous coat of plastic inside each mold, and the part is placed there until it cools.
What Is Roto-Molding Process
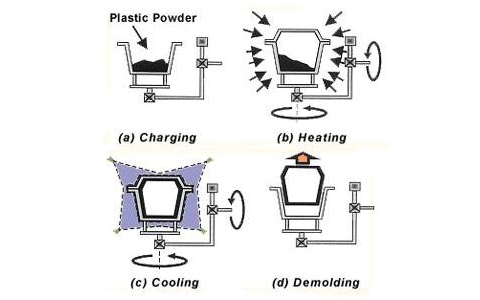
Rotational molding has a pretty straightforward principle. A plastic substance, typically in powder form, is poured into a hollow mold that is typically constructed out of sheet steel or cast aluminum. The mold is shut and slowly rotated on two axes. The polymer then gradually melts and “lays up” on the interior of the revolving mold while it is heated in an oven.
The mold is relocated to a cooling station and chilled typically with air and occasionally with a thin mist of water once the polymer powder has completely melted. The portion solidifies as the mold cools. The process is stopped, and the result is removed from the mold once the material has finally cooled down enough to loosen away from the mold surface.
Although the idea behind rotational molding is really straightforward, everyone who has ever engaged in the procedure will tell you that it is actually very difficult. The material cannot be regulated in the same way as high-pressure techniques like cleanroom injection molding because it is a casting process and there is typically no pressure involved.
Numerous factors, including ambient temperature and humidity, type of mold, material specifications, and powder quality, can have an impact on production and the final product.
How Does Rotational Molding Work?
Pellets or coarse powders are converted into fine or extra-fine powder via milling or pulverizing. The plastic material must be run through numerous pulverizers to attain the right consistency because the particle sizes of different machines vary.
Batch pulverization, dry milling or grinding, and wet pulverization are some of the several pulverization techniques. The type of molding process to which the pulverized plastic will be subjected determines the choice of pulverization technique.
The types of raw materials used in roto-molding vary depending on their physical characteristics and intended uses. In order to achieve the desired qualities and traits, additives and colors are applied. Since polyethylene is a thermoplastic that can be easily molded by heating, it is mostly employed in the roto-molding process.
The polymer, which is a powdered resin, is measured out and tightly pressed into a hollow mold. For a good flow and to avoid bubble formation, the powdered resin needs to be dry, homogenous, and in fine particle sizes. One of the elements affecting the part’s wall thickness is the amount of resin loaded.
What Does Roto-Molded Mean?
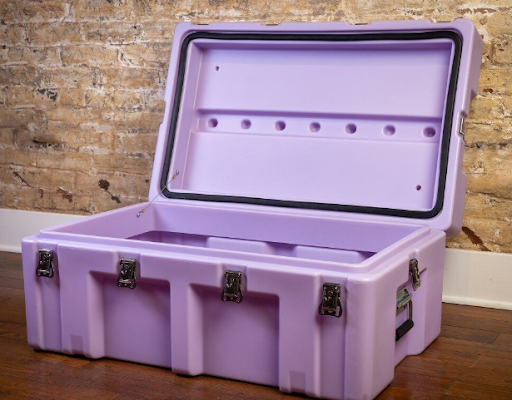

Rotomolded is another name for rotational molding, which is a manufacturing technique and is done by medical equipment parts manufacturers. It has been a long-standing practice to use this technique to create a range of plastic products and objects. Rotomolded plastic bins from TranPak are one illustration. A long number of items, including plastic toys, dolls, planters, seats, slides, canoes, storage tanks, and bins, could also be used as examples. Roto-molded is the result of the roto-molding technique.
A heated hollow mold is filled with plastic powder, which is then continually rotated until it melts and disperses uniformly across the interior corners of the mold. Both the heating and cooling processes involve rotation. After cooling, the item contracts and detaches from the mold, making removal simple.
Until recently, the process most depended on operator skill and trial-and-error to decide when the part needed to be taken out of the oven and when it was cold enough to be taken out of the mold. Since technology has advanced, it is now possible to monitor the mold’s air temperature, which eliminates a lot of the process’s guessing.
The goal of current research is to shorten cycle times while still enhancing part quality. Mold pressurization is the most exciting field. It is well known that speeding up the coalescence of the polymer particles during melting occurs when a tiny amount of internal pressure is applied to the mold.
Rotational Molding Advantages and Disadvantages

Advantages
Rotomoulding differs from conventional molding techniques in a number of distinctive ways and offers a number of benefits:
Low costs for tools: There is no pressure because this is a casting process. This indicates that molds are affordable and that modest volume might be profitable. The minimal initial cost of roto-molding makes it particularly alluring if you have a brilliant idea for a new product but are unsure of how many you will sell or simply want to produce a small number of items.
Complex shapes are simple to create: Production complications including stiffening ribs, molded inserts, and various surface textures are easily accommodated by roto-molding.
Uniform thickness of walls: Rotomoulding produces uniformly thick walls, with corners typically being thicker. This improves the integrity and strength of the product. Other techniques, like blow molding, strain the molten material at corners or sharp edges, potentially causing weak points and thin places.
Limitless size: When compared to other processes, rotational molding machine expenses are inexpensive, and the needed investment is minimal. The method allows us a lot of medical device contract manufacturing flexibility. The size of items is virtually limitless, and multiple goods can be molded simultaneously.
Disadvantages
High cycle times: Roto-molding can take up to three hours to complete one part at eight rotations per minute.
Limited choices for materials: Poly-based resins are the only materials that can be utilized for roto-molding since they can easily be transformed from granules to fine powder and have great thermal stability.
High cost of raw materials: The cost of adding the necessary additives, the expense of grinding the material into a powder, and the high criteria for thermal stability all contribute to high material costs.
Low repeatability: Due to a lack of repeatability, the roto-mold tooling’s soft metal must be repaired or replaced after 3,000 cycles, which results in quality problems.
High labor costs: Roto-molding requires more labor intensity than comparable production processes because mechanization and automation have not yet been implemented.
What Is Rotational Molding Used For

A stunning variety of moldings can be produced with this incredibly adaptable technology. Numerous industries employ rotomoulded items, which number in the hundreds. Important areas include:
- Tanks that can hold up to 50,000 liters of water and chemicals
- Products for material handling such as insulated fish and cooler boxes, crates, and pallets.
- Litter bins, road cones, bollards, traffic dividers, and road signs are examples of environmental products.
- Pontoons, buoys, and floats.
- Automobile accessories such as tractor dashboards, ducting, diesel fuel tanks, and truck mudguards.
- Canoes, kayaks, and boats
- Outdoor products like couches, water butts, and planters are available.
- Playground supplies and toys.
Along with these more conventional categories, there has been a significant increase in demand for cutting-edge, design-driven products including high-end decorative items.
Conclusion
Rotational molding also referred to as roto-molding, is a well-known molding technique that entails pushing liquid material or resin into the metallic mold while it is highly hot. The material is rotated in an oven, which stops once the resin has been poured into the interior of the mold.
You can contact Seasky Medical, leading medical injection molding companies. SeaskyMedical offers you skilled medical product development and injection molding services as an experienced medical injection firm. We work with you every step of the way, from product development to production, doing everything we can to address your concerns and lessen project risks.