Injection molding is a mainstay of modern manufacturing, producing everything from medical devices to auto parts. But behind every demanding plastic component stands a true engineering marvel: the injection mold. Far more than a simple vessel, an injection mold is a high-tech assembly of interconnected systems constructed to operate in total harmony. Knowing its main parts is crucial to designers, engineers, and anyone concerned with making a product happen. This blog will dissect the anatomy of an injection mold, looking into the all-important components that turn molten plastic into a finished product.
The Mold Base
Think of the mold base as the skeleton of the entire operation. It is the uniform, structural base on which all the other components sit in correct relationship. Typically made of pre-hardened steel, the mold base consists of a variety of plates, including the clamp plate (which mounts the mold to the injection molding machine), the “A” plate (which holds the cavity), and the “B” plate (which holds the core). The impact of a well-designed mold base is gigantic: it ensures stability during high-pressure injection process, prevents deflection, and serves as a reliable base for millions of cycles. Key points to be considered in designing it are selecting the appropriate steel grade for durability and choosing a standard or custom size appropriate for the part geometry and required mechanisms.
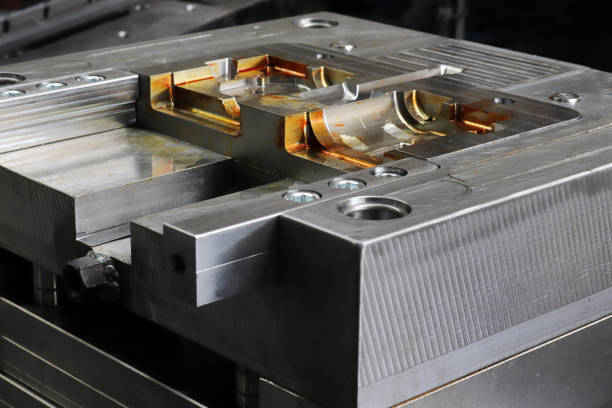
The Cavity & Core
The cavity and core are the heart of the mold—the custom-machined components that actually form the plastic part’s shape. The cavity creates the external form of the part, while the core shapes the internal features. When the mold closes, the space between them defines the part’s geometry. They work by withstanding immense heat and pressure as molten plastic is injected into the void they create. The effect is direct: their precision and surface finish determine the final part’s accuracy, detail, and texture. Design considerations are critical here, involving the selection of high-grade tool steels (like H13 or P20), intricate machining, and often advanced heat treatments to ensure a long life and resist wear from abrasive plastics.
The Injection System
The injection system is the pathway that delivers molten plastic from the molding machine’s nozzle into the mold cavities. Its main components are the sprue (the primary channel), runners (the network of channels distributing the plastic), and gates (the small, controlled entry points into each cavity). This system works by allowing the plastic to flow smoothly and fill the cavity before solidifying. The design of this system has a profound effect on part quality. Poor gate location can cause visible defects (gate vestige) and internal stresses, while unbalanced runners can lead to inconsistent filling. Design considerations focus on gate type (edge, submarine, pinpoint), runner size and shape (round is most efficient), and ensuring balanced flow to all cavities.
The Ejection System
Once the plastic has cooled and solidified, it shrinks and adheres to the core. The ejection system is the mechanism that safely pushes the finished part out of the mold. This system typically consists of ejector pins that contact the part, an ejector plate that drives the pins forward, and return pins that retract the ejector pins when the mold closes again. It works by activating after the mold opens, applying a controlled force to release the part. The effect of a well-designed system is a clean, automatic release without damaging the part. Design considerations include the placement of ejector pins to avoid marks on critical surfaces, applying sufficient force without bending the part, and ensuring the system reliably resets for the next cycle.
The Cooling System
The cooling system is arguably the most critical factor for determining the profitability of a molding project. It consists of a network of channels drilled through the mold plates (especially the cavity and core) through which a coolant (usually water or oil) is continuously circulated. It works by extracting heat from the molten plastic, causing it to solidify quickly so the part can be ejected. The effect is twofold: efficient cooling drastically reduces the cycle time, increasing production speed, while uniform cooling prevents defects like warping, sink marks, and internal stresses. Design considerations involve carefully planning the channel layout to follow the part’s contours, ensuring even cooling, and selecting the right coolant temperature for the specific polymer being used.
The Guiding & Alignment System
Imagine the tremendous forces involved as a mold closes at high speed. The guiding and alignment system ensures that the two halves of the mold meet perfectly every time, preventing catastrophic damage to the core and cavity. The primary components are leader pins and bushings. The hardened steel leader pins on one half of the mold slide into precisely machined bushings on the other half, guiding the mold into perfect alignment before the surfaces touch. The effect is the protection of delicate mold components and the production of parts with consistent wall thickness. Design considerations include the number and diameter of the pins (typically four) to resist lateral forces and the use of additional interlocks for critical alignment.
The Venting System
As molten plastic rushes into the cavity, it must displace the air already inside. If the air cannot escape, it becomes trapped and compressed, leading to serious defects. The venting system provides a controlled escape route for this air. These are very shallow grooves (often only 0.01-0.03 mm deep) machined at the parting line or into ejector pins. They work by allowing air to pass through while being shallow enough to block the much more viscous plastic. The effect is the prevention of burns (diesel effect from compressed air), short shots (incomplete filling), and poor surface finishes. Design considerations involve placing vents at the end of fill paths and ensuring their depth is appropriate for the plastic material’s viscosity.
Seasky Medical – Your Trusted Medical Injection Molding and Mold Manufacturer in China
When precision, quality, and regulatory compliance are non-negotiable, choosing the right manufacturing partner is critical. Seasky Medical specializes in high-precision injection molds and molded components for the medical industry. We understand the critical tolerances, material biocompatibility, and rigorous validation requirements of medical applications. From mold design to final production, Seasky Medical is committed to being your reliable and innovative manufacturing partner in China.
Conclusion
An injection mold is a masterpiece of integrated engineering, where each component plays a vital role in the success of the manufacturing process. From the structural mold base and the forming cavity/core to the critical supporting systems for injection, ejection, cooling, alignment, and venting, every element must be meticulously designed and manufactured. Understanding these components not only provides insight into how everyday products are made but also highlights the complexity and expertise required to produce high-quality, cost-effective plastic parts. It is the seamless interaction of these systems that makes injection molding such a powerful and ubiquitous manufacturing technology.